
The city of Aden (Bilal Al-Sabri)
06-07-2023 الساعة 11 صباحاً بتوقيت عدن
"This requires political decisions such as the transition to low-carbon energy and encouraging highly efficient technologies"
Raad Alrimi (South24)
The capital, Aden, is one of the hottest and most humid cities in the country. The city has gained these features due to its coastal location overlooking the Gulf of Aden and its place in the tropical region. The hot season in this city is a matter of concern for people annually, especially over recent years with the outbreak of war and the collapse of the service system. Particularly, this included electricity which constitutes an ongoing dilemma for residents.
Although Aden's geographical features justify a big part of the causes for its high heat and humidity along with the worldly climate changes and global warming, environment experts believe that the escalation of temperature and humidity levels in Aden over past periods is probably a result of unnatural reasons related to the wrong human activities and the lack of interest in the city's weather.
Experts enumerate the most prominent causes which can be divided into several aspects. This includes growing environmental pollution, the imbalances of the urban planning required for the coastal city to meet the global standards in other similar cities, and the intensified rise in population and slums due to the waves of internal displacement and external immigration. These causes walk along with governmental neglect.
The experts participating in this report proposed some treatments that could contribute to reducing and mitigating Aden’s weather, especially in summer.
Hard weather
Each year, the hot season reaches its peak in the middle months, especially between April and September. The temperatures that sometimes exceed 40°c in daylight and the humidity that reaches the level of 73% constitute an onerous duet for people during the hot season, especially with the weak electricity service used by people to cool homes and confront summer.
Aden derives this weather from its geographical location which is defined at 12.47 north latitude. This means that Aden is located within the tropical region. This exposes it to the largest amount of solar rays throughout the year. Its exposed surface is composed of volcanic rocks and surrounded by large water bodies that play an active role in the amounts of received and lost solar rays.
Aden suffers from a paucity of rain. In general, rainfall is few in Aden and it often happens in winter and spring while it is rare in summer. The general rate of average rainfall in the city is 50 mm.
Abdulsalam Al-Jaabi, Undersecretary of the General Authority for Environmental Protection in the Yemeni government, stressed that the temperatures in Aden have climbed over the past decades due to global climate changes. He told "South24" Center: "The main reason for the high temperatures in Aden is its closeness to the equator, but the remarkable rise is due to climate changes".
International climate expert Dr. Abdulqadir Al-Kharaz, former head of the General Authority for Environmental Protection in Yemen, said: "Yemen is among the countries most vulnerable to the global climate change impact". He told "South24 Center": "Over the past period, Yemen witnessed many changes, including high temperatures in summer that compared to the levels of ten years ago".
He added: "There have been changes in the rates of rain levels in the mountainous and desert regions. They increased in the mountainous regions and decreased in the desert regions. The rainy seasons in the coastal regions have changed from summer to winter, which means higher summer temperatures in Aden, Hodeidah, and other coastal areas in the country".
In May, a study published by "Nature Sustainability" warned of the increase of temperatures in Yemen and Gulf states over the coming years.
Regarding the Middle East, the study concluded that "100% of land and people in Bahrain, Qatar, and the UAE are subject to life-threatening temperatures along with the global temperature rise by 2.7 °C".
The study indicated that the UAE is particularly at risk. 80% of its people suffer from hot weather, even amid the 1.5 °C scenario. Moreover, Kuwait, Oman, and Yemen are highly vulnerable to global warming.
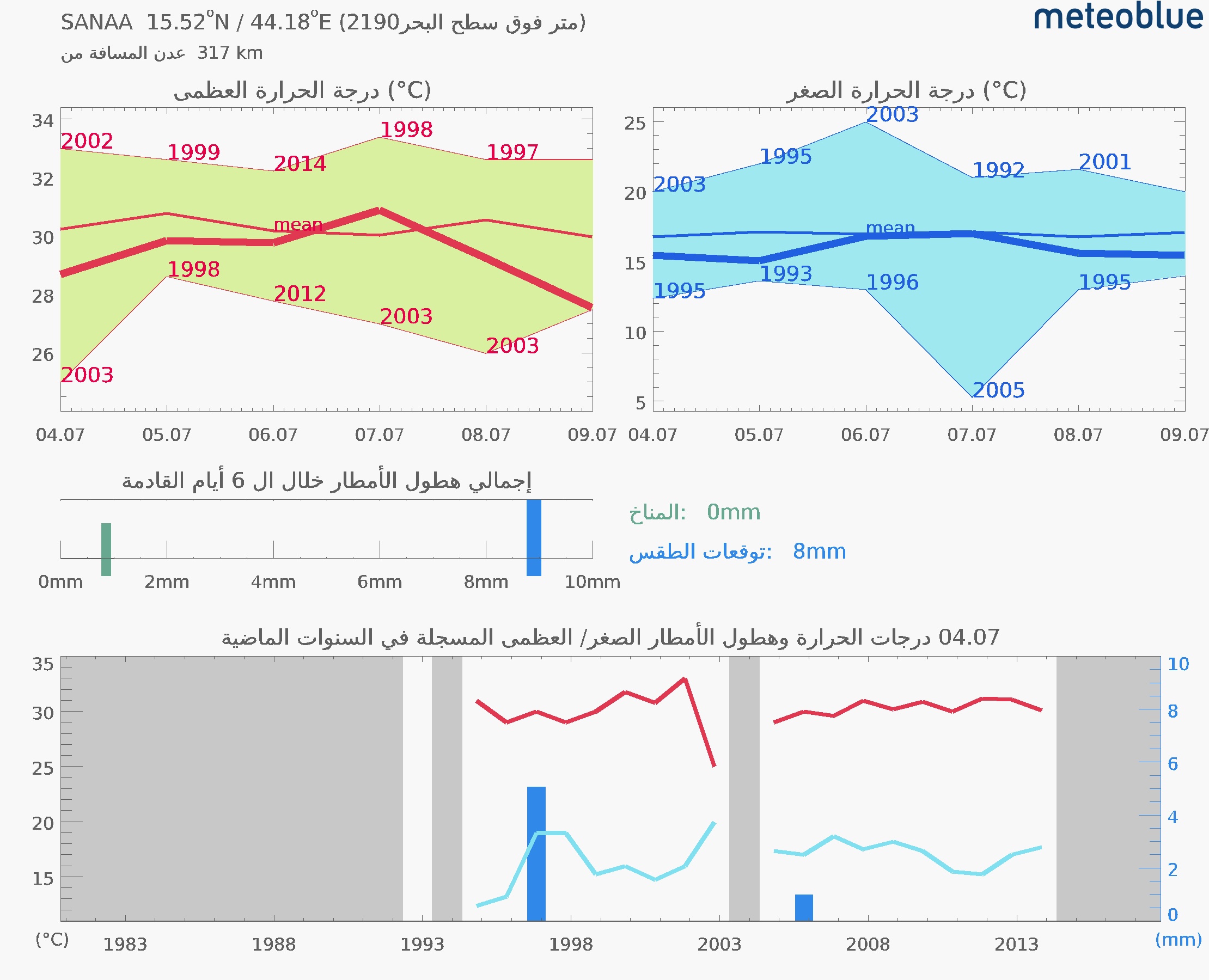
The changes in temperatures and weather in Aden over the past decades (Meteoblue)
Dr. Abdulraqib Al-Akishi, Adaptation Manager at the General Authority for Environmental Protection in Yemen, pointed out that the city’s coastal location makes it "a hot island". He told "South24 Center" that "the coastal cities, in general, are hotter than the mountainous ones. Temperatures in the coastal cities exceed the neighboring regions even if they are similar in geographical location and climate. The difference in temperatures is between 5-15 °c".
"There are no exclusive studies for Aden. If climate data over the past 30 years are available, maps that explain this matter can be designed. Emotionally, people can say that temperatures are higher than before. This can be true, but it needs a study to confirm it", he added.
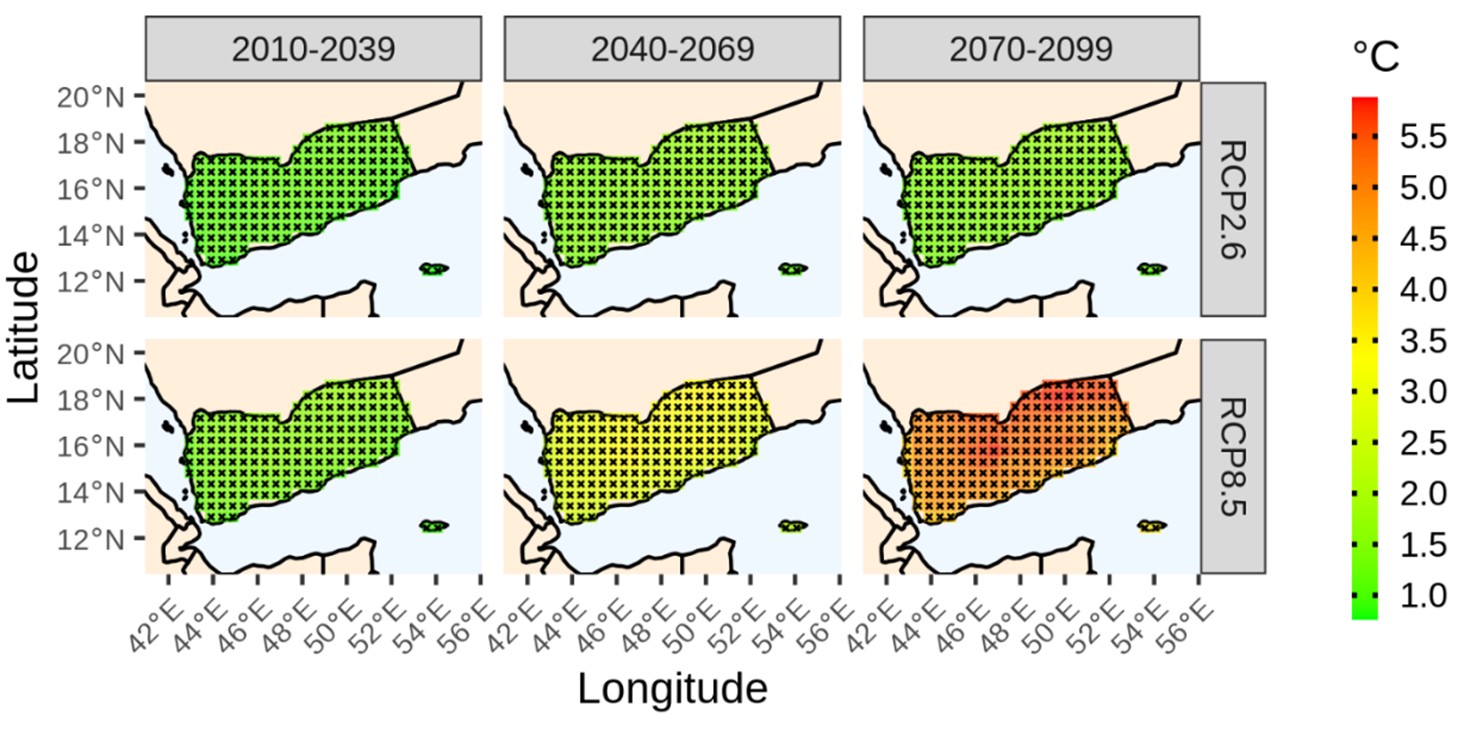
Based on the open environmental sources seen by the writer, it is expected that temperatures will increase over the coming years in Aden more than their current levels as shown in the following figure that expects temperature changes according to the most pessimistic emission scenarios". "RCP 2.6".
The maps of this expected scenario show a 2-3 °c increase in temperature over the next 10 years.
Local causes
According to urban planning expert Hassan Al-Hadithi, there are local reasons exclusive to Aden that exacerbate the hot weather problem in the city along with the external factors related to Aden's geographical location and the world climate changes resulting from global warming which casts a shadow over different states and cities".
The expert said: “One of the reasons that make cities less hot is their design and construction quality. This type of planning is absent in the random and crowded cities, which is what the capital city Aden suffers from".
He added: "The reasons also include the ways of building and the quality of the used materials. This affects temperatures. In well-planned cities, there is a focus on selecting building materials, such as cement and paint that have been tested and proven to help reduce temperatures rather than exacerbate them".
He noted that "Word Health Organization recommends 0.5-2 hectares of green areas for each resident in cities and that people should live not less than 300m away from green areas. Aden suffers from the lack of prior urban planning that considers its geographical location and climate as well as the lack of green areas".
He pointed to "other problems such as wasted sewage that can be exploited in enhancing the green areas".
"It is difficult to count the activities of people that may contribute to the increase of temperatures in the city. However, temperatures in general are higher in industrial and crowded areas. In general, this is not attributed to people but to planning decisions for the city such as determining the place and quality of building as well as maintaining a big distance between residential areas and factories as well as power plants", according to him.
Al-Akishi believes that car exhaust contributes to the rise of temperatures in Aden which has thousands of used cars imported from abroad at cheap prices and leaving harmful emissions in the air".
Reducing temperatures
According to Al-Jaabi, "temperatures in Aden or other cities can be largely reduced. Some treatments can help citizens and residents, as well as the ecosystem, to adapt to changes in temperature. These practices include afforestation and urban planning that support the adaptation of the ecosystem in Aden".
Al-Jaabi acknowledges the lack of the government's interest in environmental issues. He added: "The issues of environment, climate, and global warming are not a priority for the government compared to other issues such as education, health, and the humanitarian crisis. However, it is important to add environmental issues among the government's priorities in the coming years, especially in Aden".
Dr. Al-Akishi stressed that "climate change issues are the responsibility of decision-makers in the first place". He concluded: "This requires political decisions such as the transition to low-carbon energy and encouraging highly efficient technologies in using energy, whether in lighting, transportation or others. A positive status for climate, weather, and heat can be created if there is the will to do so".
Journalist at South24 Center for News and Studies