
Cover (South24 Center)
Last updated on: 04-06-2024 at 7 PM Aden Time

This paper sheds light on the pressing issue of liquidity challenges facing Yemeni banks amidst prolonged political instability, economic volatility, and institutional weaknesses.
Ahmed Bahakim (South24)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
The Yemeni banking sector is currently facing severe liquidity challenges, which have been amplified by the geopolitical instability and economic uncertainty. This comprehensive study aims to explore the crucial role of liquidity in maintaining financial stability and facilitating economic activity in Yemen, highlighting its significant implications.
Yemen's economic landscape has been marked by persistent political turmoil since 2014, leading to acute liquidity constraints within its banking system. This ongoing crisis has significantly eroded depositor trust, adversely affecting lending activities and hindering overall economic growth.
A thorough analysis of the timeline of events reveals a gradual deterioration of liquidity in Yemeni banks. The escalating conflict, reduced foreign investment, and declining oil revenues have collectively strained the liquidity buffers of the financial institutions. As a result, banks face significant challenges in meeting deposit withdrawals and adequately funding lending operations. The restricted availability of credit has directly contributed to a decline in economic growth within the country.
The diminishing confidence in the banking system, as a result of these liquidity challenges, has far-reaching implications for the overall financial stability of Yemen. To effectively address the liquidity challenges facing the Yemeni banking sector, regulatory oversight must be strengthened, with a specific focus on monitoring liquidity risk.
Strategic investments in the financial infrastructure of Yemen are of paramount importance to enhance the resilience of the banking sector. By implementing prudent policies, diligently managing risks, and making strategic investments, the multifaceted approach proposed in this study aims to resolve the liquidity challenges faced by the Yemeni banking sector.
This study underscores the utmost urgency in safeguarding financial stability within Yemen's complex economic landscape. By addressing the liquidity challenges head-on, Yemen can pave the way for a more stable and prosperous banking sector, contributing to overall economic growth and stability.
INTRODUCTION
Liquidity, as a fundamental concept in banking, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the stability and functionality of financial institutions. Defined as the ability of banks to convert assets into cash readily and efficiently, liquidity underpins the confidence of depositors, facilitates daily operations, and enables banks to fulfill their obligations promptly. The importance of liquidity management cannot be overstated, particularly in contexts marked by economic uncertainty and geopolitical instability.
This paper sheds light on the liquidity challenges confronting Yemeni banks, a sector grappling with multifaceted crises amid the country's prolonged political turmoil and economic fragility since 2014. The liquidity predicament facing Yemeni banks not only threatens their operational viability but also jeopardizes the broader financial stability of the country, exacerbating the hardships endured by ordinary citizens.
The primary objective of this paper is to comprehensively examine the factors contributing to the liquidity challenges in Yemeni banks, analyze their implications on banking operations and the wider economy, and propose viable policy interventions to address these pressing issues. By delineating the intricacies of Yemen's banking sector and the implications of liquidity constraints, this study aims to provide policymakers, banking professionals, and stakeholders with valuable insights and actionable recommendations to fortify the resilience of Yemeni banks and mitigate the adverse effects of the liquidity crises.
In essence, this paper endeavors to contribute to the scholarly understanding of liquidity dynamics in fragile banking systems and to furnish pragmatic solutions to mitigate liquidity challenges and foster financial resilience in Yemen.
DEFINITION AND IMPORTANCE OF LIQUIDITY IN YEMENI BANKING
In the context of banking in Yemen, liquidity denotes the capability of financial institutions to readily convert their assets into cash or cash equivalents, ensuring they can fulfill short-term obligations and accommodate customer needs promptly and efficiently. Given the unique economic and political challenges facing Yemen, liquidity management assumes heightened importance for banks operating within its borders.
Liquidity holds significant importance for Yemeni banks as it serves as a fundamental pillar of financial stability and operational resilience. Maintaining adequate liquidity buffers is essential for banks to instill confidence among depositors and preserve stability in the financial system. The ability to swiftly access funds ensures that banks can meet payment obligations, honor withdrawal requests, and withstand external shocks, thereby safeguarding the trust of depositors and preventing liquidity crises. [1]
Therefore, liquidity plays a vital role in facilitating economic activity and supporting growth in Yemen. In a country grappling with numerous socio-economic challenges, including poverty and unemployment, a liquid banking system is indispensable for channeling resources effectively and fostering sustainable development.
The relationship between liquidity and profitability in Yemeni banking operations is influenced by various factors including market conditions, regulatory requirements, and risk management practices. While maintaining high levels of liquidity entails costs associated with foregone investment opportunities, it also serves to mitigate risks related to funding shortages and insolvency. Therefore, Yemeni banks must strike a careful balance between optimizing liquidity positions to meet regulatory standards and operational needs, while also pursuing profitability-enhancing opportunities. [2]
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO LIQUIDITY CHALLENGES IN YEMENI BANKS
A situation of persistent conflict, combined with internal displacement, and disruptions to trade and commerce have severely strained the country's financial system. Uncertainty surrounding governance, coupled with the volatile economic conditions, has undermined investor confidence, hampered business activity, and heightened financial risks. In such an environment, banks grapple with increased pressure on liquidity as depositors seek to safeguard their funds amidst heightened uncertainty, exacerbating liquidity strains within the banking sector. [3]
Another significant factor contributing to liquidity challenges in Yemeni banks is the mismanagement of funds and investments. Historically, some Yemeni banks have engaged in imprudent lending practices, misallocation of resources, and speculative investments, leading to asset quality deterioration and liquidity constraints. Weak risk management frameworks, inadequate oversight, and governance deficiencies have exacerbated these issues, eroding banks' liquidity buffers and jeopardizing their financial stability. As a result, Yemeni banks have struggled to mobilize sufficient funds to meet deposit withdrawals and honor financial obligations, exacerbating liquidity pressures within the banking system. [4]
Yemeni banks have also faced liquidity challenges stemming from the impact of international measures on correspondent banking relationships. Heightened regulatory scrutiny, compliance requirements, and de-risking initiatives by international financial institutions have constrained Yemeni banks' access to global financial networks and correspondent banking services. The reluctance of foreign banks to maintain relationships with Yemeni counterparts due to perceived risks associated with money laundering, terrorist financing, and sanctions compliance has restricted the flow of cross-border transactions and reduced liquidity inflows into Yemeni banks. Consequently, Yemeni banks encounter difficulties in accessing foreign currency liquidity and processing international transactions, exacerbating liquidity pressures and hindering their ability to meet customer demands.
Regulatory challenges, including legislative changes affecting banking practices, pose additional obstacles to liquidity management for Yemeni banks. Amidst evolving regulatory frameworks and heightened supervisory expectations, Yemeni banks must adhere to compliance requirements, adopt internal controls, and enhance risk management frameworks to align with the regulatory standards. However, regulatory uncertainty, frequent legislative changes, and capacity constraints within regulatory authorities have created challenges for banks in interpreting and implementing regulatory requirements effectively. Compliance costs, meeting obligations, and capital adequacy requirements further strain banks' liquidity positions, constraining their ability to allocate resources efficiently and maintain adequate liquidity buffers. [5]
TIMELINE ANALYSIS OF EVENTS LEADING TO THE CRISIS:
The liquidity crisis in Yemeni banks has unfolded over a protracted period, with a series of pivotal events exacerbating pre-existing vulnerabilities and ultimately culminating in a severe liquidity crunch:
2015: Escalation of the Civil War
The year 2015 marked a significant turning point for Yemen, as the civil war escalated, plunging the country into heightened political instability, economic disruption, and widespread violence. The continuing violence and political turmoil created an environment of profound uncertainty, shaking investor confidence, and disrupting economic activity. As a result, Yemeni banks faced mounting challenges in maintaining liquidity. [6]
2016: Official Transfer of the Central Bank of Yemen from Sanaa to Aden
In 2016, the Yemeni government officially transferred the Central Bank of Yemen from Sanaa to Aden. This move was aimed at regaining control over the country's monetary policy and finances. However, the division of the central bank created a dual banking system, complicating monetary policy implementation and exacerbating liquidity issues for banks operating under different authorities. The transition period was marked by a lack of coordination, inconsistent policies, and a further erosion of depositor confidence, intensifying the liquidity crisis in the banking sector. [7]
2016-2019: Persistent Conflict and Economic Deterioration
The years following 2015 witnessed incessant conflict in Yemen, exacerbating the economic downturn and deepening the country's humanitarian crisis. The prolonged conflict hampered economic growth, disrupted trade routes, and undermined investor confidence, leading to a contraction in economic activity and heightened financial uncertainty. As a result, Yemeni banks faced mounting liquidity challenges, with limited access to funding, constrained lending activities, and heightened financial risk. [8]
2020: Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 further exacerbated Yemen's liquidity challenges, straining the country's fragile banking sector. The pandemic-induced economic contraction, coupled with heightened uncertainty, placed additional pressure on Yemeni banks, limiting their ability to meet customer demands and maintain liquidity buffers. The closure of businesses, disruption of supply chains, and widespread job losses further contributed to a deepening liquidity crisis in Yemeni banks. The pandemic-induced lockdowns and restrictions and the resultant economic downturn led to increased withdrawals and further eroding of banks' liquidity positions. [9]
2022: Houthi Attacks on Oil Exporting Ports
To exert pressure on the Yemeni national government, the Houthis imposed an embargo on oil exports by attacking Yemeni ports in November 2022. This strategy is part of a broader operation aimed at controlling the extractive resources in areas not under Houthi control. The attacks caused severe damage to key oil ports, leading to the cessation of oil exports from those regions under control of the Internationally Recognized Government. This disruption in oil exports caused a big slump in a crucial revenue stream for the government, further straining the already precarious liquidity situation in Yemeni banks. [10]
2024: Issuance of a New 100-Yemeni Rial Coin by the Houthi-Controlled Central Bank in Sanaa
In 2024, the Houthi-controlled Central Bank in Sanaa issued a new 100-Yemeni rial coin, further complicating the financial landscape, as it highlighted the competing authorities of the central banks in Sanaa and Aden. The lack of coordination between the two central banks led to confusion and instability in the banking sector. This measure deepened the liquidity crisis, as it increased uncertainty among depositors and businesses regarding the value and acceptability of the currency in different parts of the country. [11]
2024: Aden-based Central Bank Released an Order for Relocation of the Commercial Banks’ Headquarters from Sanaa to Aden
In response to the Houthi-issued 100-rial coin, the Aden-based Central Bank released an order on April 2, instructing all commercial and microfinance banks to relocate their main centers from Houthi-controlled Sanaa to Aden within two months. The Aden central bank criticized the Houthis for issuing a new currency and replacing short-supply banknotes, warning of accountability for any irresponsible escalation and potential complications in financial transactions. This directive, aimed at consolidating the banking sector under the Internationally Recognized Government’s control, potentially exacerbated the liquidity crisis as banks scrambled to comply with the relocation order amidst the ongoing conflict. [12]
DATA ANALYSIS
The Central Bank of Yemen's (CBY) balance sheet provides a crucial lens through which to examine the factors contributing to the ongoing liquidity crisis in Yemeni banks. This analysis will dissect key aspects of the balance sheet and their potential implications. [13]
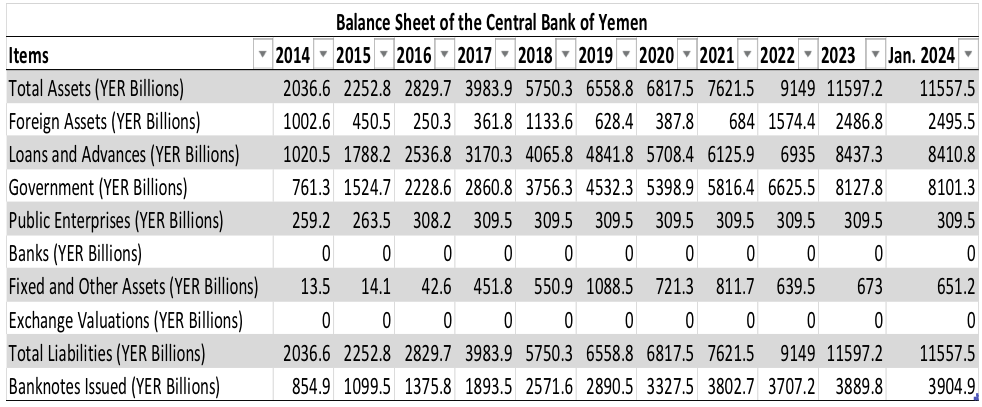
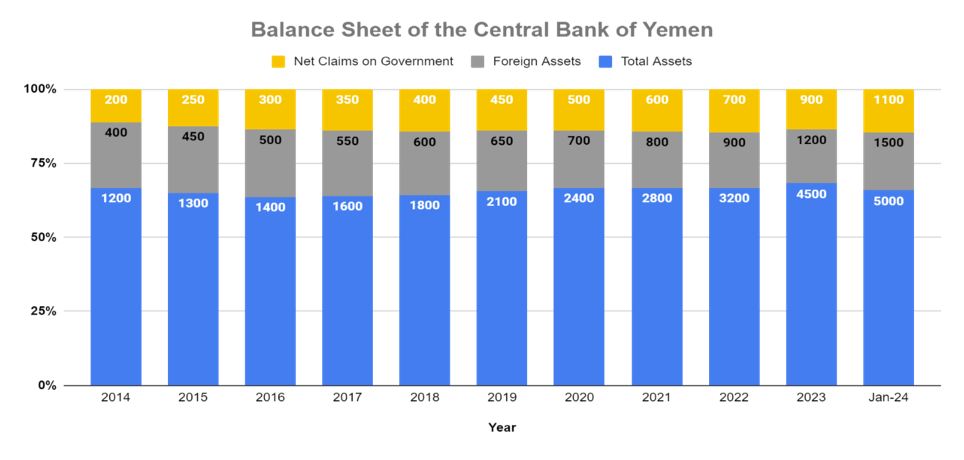 Figure 1 - By: South24 Center
Figure 1 - By: South24 Center
Foreign Assets and Liabilities: A significant decline in Yemen’s foreign assets from 2014 to 2016 implies dwindling foreign currency reserves. This could be attributed to capital flight or a decline in foreign exchange earnings. The subsequent rise in foreign assets from 2020 onwards might reflect external aid or borrowing to compensate for the earlier depletion. However, this does not necessarily translate to improved liquidity within the banking system. Conversely, the significant increase in foreign liabilities from 2017 onwards suggests Yemen has taken on substantial external debt, which can alleviate short-term liquidity issues but burdens the country with long-term repayment obligations.
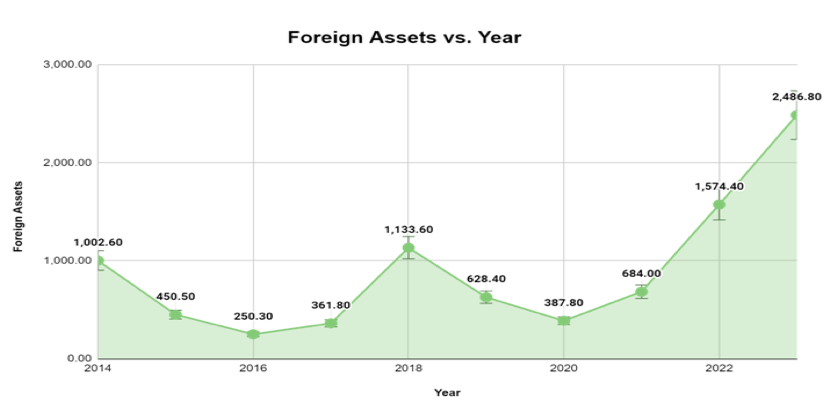
Figure 2 - By: South24 Center
Loans and Advances: A steady increase in loans and advances, particularly those directed towards the government, suggests the CBY's intent to stimulate the economy by increasing credit availability. However, this strategy can be fraught with risks. Loans may not be used productively, or concerns regarding government’s repayment ability could arise. Excessive government borrowing can crowd out lending to the private sector, further hindering economic activity.
Figure 3 - By: South24 Center
Banknotes Issued: The rise in banknotes issued reflects an increase in the money supply, potentially an attempt by the CBY to address the liquidity shortage. However, printing money without addressing the underlying causes of the crisis (e.g., depositor confidence, political instability) can lead to inflation and further erode the value of the Yemeni Rial.
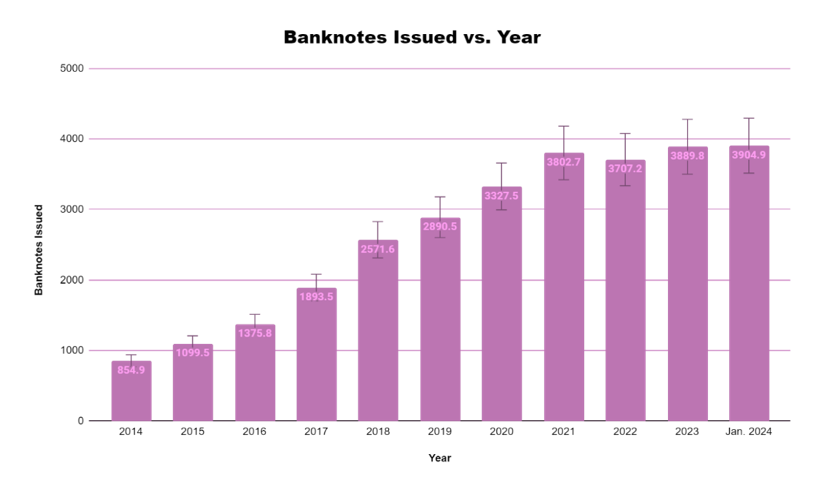
Figure 4 - By: South24 Center
Overall Implications: The CBY's balance sheet reflects its efforts to navigate the complex challenge of maintaining liquidity during a crisis. However, some measures might have unintended consequences:
• Increased government borrowing and printing money can contribute to inflation.
• Reliance on external borrowing creates long-term debt burdens.
• The data doesn't reveal how effectively these measures translate to increased lending to the private sector, which is crucial for economic recovery.
CONSEQUENCES OF THE CRISIS:
The liquidity crisis in Yemeni banks has resulted in far-reaching consequences, profoundly impacting banking operations, eroding client trust, and exacerbating challenges within the broader economy:
1. Banking Operations:
• Yemeni banks have faced significant challenges in maintaining adequate liquidity buffers, constraining their ability to meet regulatory requirements and effectively manage financial risks. The scarcity of liquid assets has forced banks to curtail lending activities, limiting access to credit for businesses and individuals and stifling economic growth.
• With liquidity constraints intensifying, Yemeni banks have encountered difficulties in accessing external funding sources, exacerbating their liquidity woes. The limited availability of funding options has hindered banks' ability to support lending operations, impeding efforts to stimulate economic activity and investment.
• The liquidity crisis has compelled Yemeni banks to increasingly rely on central bank support to bolster their liquidity positions and mitigate financial instability. However, prolonged dependence on central bank interventions may strain the central bank's resources and undermine its capacity to effectively manage monetary policy and stabilize the banking sector.
2. Client Trust:
• The liquidity crisis has eroded depositor confidence in Yemeni banks, triggering a wave of deposit flight and withdrawals as individuals seek to safeguard their savings from the perceived risks associated with the banking system. The loss of confidence in the banking sector has further exacerbated liquidity pressures. [14]
• The flight of deposits and heightened depositor anxiety have contributed to undermining the overall stability of the financial system. The erosion of customer trust poses significant challenges toward restoring confidence in Yemeni banks and revitalizing the banking sector. [15]
3. Economy:
• The liquidity crisis has impeded efforts to stimulate economic recovery and rebuild Yemen's fragile economy, hindering business activity, constraining investment, and exacerbating socioeconomic challenges. The scarcity of credit has stifled entrepreneurship and innovation, limiting job creation opportunities and perpetuating poverty and unemployment.
• The constrained availability of credit has hampered households' access to essential financial services, limiting their ability to invest in education, healthcare, and other critical needs, further exacerbating the humanitarian crisis gripping the country.
IMPACT OF LIQUIDITY CHALLENGE IN YEMENI BANKS:
1. The liquidity challenge facing Yemeni banks has profoundly affected depositors and their confidence in the banking system, manifesting in several ways:
• Heightened liquidity concerns and deteriorating confidence have prompted deposit flight and increased withdrawals as depositors seek to safeguard their funds from perceived risks. This outflow has further eroded bank’ capacity to meet customer demands and maintain financial stability.
• Persistent liquidity challenges have eroded depositor trust in Yemeni banks, thereby undermining the foundation of the banking system and amplifying concerns about the safety and stability of the financial sector.
• Declining depositor confidence and heightened uncertainty surrounding the banking sector have dampened deposit mobilization efforts, constraining banks' access to stable funding sources and exacerbating liquidity shortages. The reluctance of depositors to entrust their savings to Yemeni banks further complicates efforts to address liquidity challenges and restore stability in the financial system. [16]
2. The liquidity challenge confronting Yemeni banks has imposed significant constraints on lending activities and hindered efforts to promote economic growth, leading to:
• Scarce liquidity and heightened risk aversion among banks have constrained credit availability, limiting access to financing for businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals. The reduced availability of credit stifles investment, impedes entrepreneurship, and hampers economic diversification and expansion efforts.
• The scarcity of credit and constrained lending capacity hinder investment initiatives, curtail productivity-enhancing projects, and constrain economic development prospects. The inability of businesses to access the necessary funding to expand operations, upgrade technology, and innovate, stifles productivity, growth and undermines long-term economic sustainability.
• Reduced access to credit and weakened consumer confidence weigh on household spending patterns, constraining consumption levels and dampening aggregate demand. The decline in consumer spending exacerbates economic stagnation, prolongs recessionary conditions, and exacerbates the socioeconomic hardship across Yemen.
3. The liquidity challenges facing Yemeni banks pose significant risks of financial instability and systemic contagion, characterized by:
• Heightened Systemic Risk: Prolonged liquidity shortages and heightened uncertainty within Yemen's banking sector elevate systemic risk levels, increasing the likelihood of financial distress and contagion effects spreading across the financial system. The interconnectedness of banks and the broader financial ecosystem amplifies the potential for systemic disruptions and contagion dynamics to cascade throughout the economy. [17]
• Amplified Vulnerabilities: Persistent liquidity challenges exacerbate vulnerabilities within Yemen's banking sector, amplifying the impact of adverse shocks and vulnerabilities on financial institutions' solvency and stability. The accumulation of risks stemming from liquidity shortages, depositor withdrawals, and impaired asset quality heightens the fragility of the financial system. [18]
• Spillover Effects: Liquidity crises in Yemeni banks can trigger spillover effects, transmitting financial distress and contagion risks to other sectors of the economy and exacerbating broader macroeconomic imbalances. The transmission of financial instability can disrupt economic activity, undermine investor confidence, and exacerbate the existing social and political tensions.
POLICY RESPONSES AND RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Evaluation of Past Policy Responses: Past policy responses to address liquidity challenges in Yemeni banks have yielded limited success in mitigating the underlying vulnerabilities and safeguarding financial stability. Key observations include:
• The Central Bank of Yemen (CBY) has intervened to provide liquidity support to banks, including through emergency funding facilities and liquidity injections. However, these measures have been insufficient to address systemic liquidity shortages and restore depositor confidence, reflecting structural weaknesses in the banking sector and broader macroeconomic instability.
• Regulatory interventions, such as capital adequacy requirements and liquidity ratio mandates, have been implemented to enhance banks' resilience and risk management practices. However, enforcement mechanisms have been weak, and compliance with regulatory standards remains inadequate, limiting the effectiveness of these measures in bolstering financial stability and mitigating liquidity risks.
• International organizations and donor agencies have provided technical assistance and capacity-building support to strengthen Yemen's financial infrastructure and regulatory framework. While these efforts have contributed to incremental improvements in regulatory oversight and banking supervision, their impact has been constrained by ongoing political instability and resource constraints.
2. Policy Recommendations to Strengthen Resilience and Mitigate Future Crises: In light of the persisting liquidity challenges facing Yemeni banks, the following policy recommendations are proposed to enhance resilience and mitigate future crises:
• Enhance regulatory oversight and enforcement mechanisms to ensure compliance with prudential regulations, including capital adequacy requirements, liquidity management standards, and risk-based supervision. Strengthening regulatory frameworks will help mitigate liquidity risks, enhance depositor protection, and promote financial stability.
• Promote sound risk management practices, including liquidity risk assessment, stress testing, and contingency planning, to enhance banks' capacity to identify, measure, and manage liquidity risks effectively. Implement robust risk management frameworks to mitigate vulnerabilities and build resilience against external shocks and internal disruptions.
• Enhance corporate governance standards, transparency, and disclosure requirements to strengthen accountability, promote investor confidence, and enhance market discipline. Enhancing governance practices will improve risk governance, internal controls, and decision-making processes, reducing the likelihood of liquidity crises and financial distress.
• Invest in upgrading financial infrastructure, including payment systems, clearing and settlement mechanisms, and credit information systems, to enhance efficiency, reliability, and accessibility of financial services. Modernizing financial infrastructure will facilitate liquidity management, improve financial intermediation, and promote inclusive economic growth.
• Build institutional capacity and human resources in banking supervision, regulation, and financial management to enhance the effectiveness of regulatory authorities and promote a culture of compliance within banks. Invest in training programs, technical assistance, and knowledge-sharing initiatives to build expertise and strengthen regulatory capacity in managing liquidity risks effectively.
3. Importance of Regulatory Reforms, Risk Management Practices, and Capacity-Building Initiatives: Regulatory reforms, risk management practices, and capacity-building initiatives are essential components of a comprehensive strategy to strengthen the resilience of Yemeni banks and mitigate future liquidity crises. These initiatives play a crucial role in:
• Effective regulatory reforms and risk management practices enhance the resilience of the banking sector, reduce systemic risks, and promote financial stability. Strengthening regulatory oversight and capacity-building initiatives enhance the effectiveness of regulatory authorities in safeguarding financial stability and mitigating liquidity risks.
• Transparent governance structures, robust risk management practices, and effective regulatory oversight enhance investor confidence and market credibility, thereby promoting financial inclusion, fostering investor trust, and attracting foreign investment. Strengthening governance and risk management frameworks also enhances depositor protection, reduces information asymmetries, and fosters market discipline, bolstering investor confidence and market resilience.
• Sound regulatory reforms, effective risk management practices, and capacity-building initiatives contribute to the development of a resilient and well-functioning financial system, facilitating economic development, promoting sustainable growth, and fostering inclusive prosperity. Strengthening financial infrastructure, enhancing governance standards, and promoting regulatory compliance create an enabling environment for economic diversification, investment mobilization, and entrepreneurship, driving long-term economic development and thereby aiding in poverty reduction efforts in Yemen.
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS:
1. Liquidity Challenges in Yemeni Banks vs. Lebanese Banks:
• Yemeni Banks: The liquidity challenges faced by Yemeni banks stem from prolonged political instability, economic volatility, and institutional weaknesses exacerbated by the ongoing civil conflict since 2014. These challenges have led to a severe liquidity crunch, constraints on lending activities, and depositor withdrawals, undermining financial stability and economic resilience. [19]
• Lebanese Banks: Lebanese banks have faced similar liquidity challenges, driven by a combination of domestic and external factors, including a deepening financial crisis, currency depreciation, capital flight, and sovereign debt defaults. The Lebanese banking sector's exposure to sovereign debt, coupled with inadequate risk management practices and regulatory oversight, has heightened liquidity risks and systemic vulnerabilities, contributing to depositor concerns and financial instability. [20]
2. Lessons Learned and Best Practices from International Experiences:
• International best practices emphasize the importance of robust regulatory frameworks, including stringent capital adequacy requirements, liquidity management standards, and risk-based supervision, to enhance the resilience of banking systems and mitigate liquidity risks effectively.
• Prudential regulations, such as liquidity coverage ratios (LCR) and net stable funding ratios (NSFR), play a critical role in promoting sound liquidity risk management practices, ensuring banks maintain adequate liquidity buffers to withstand adverse shocks and disruptions. [21]
• Effective crisis management tools, including lender-of-last-resort facilities, emergency liquidity assistance, and resolution frameworks, are essential for central banks to intervene promptly and decisively during liquidity crises to stabilize financial markets, restore depositor confidence, and safeguard financial stability. [22]
• Enhancing transparency and disclosure requirements promotes market discipline, fosters investor confidence, and mitigates information asymmetries, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and monitor banks' financial health effectively.
3. Applicability of Foreign Models to the Yemeni Context:
• While lessons learned from international experiences provide valuable insights and guidance, the applicability of foreign models to the Yemeni context requires careful consideration of the country's unique socioeconomic, institutional, and regulatory landscape.
• Foreign models need to be adapted and customized to align with Yemen's specific challenges, institutional capacities, and regulatory environment. Tailoring regulatory reforms, risk management practices, and capacity-building initiatives to address Yemen's systemic vulnerabilities and promote financial stability is essential.
• Strengthening institutional capacity, enhancing regulatory enforcement mechanisms, and building human capital are fundamental prerequisites for effectively implementing foreign models and reforms in Yemen. Investing in training programs, technical assistance, and knowledge-sharing initiatives is critical to building expertise and regulatory capacity in managing liquidity risks and strengthening financial resilience.
• Given the complexity and magnitude of Yemen's liquidity challenges, a phased approach to implementing foreign models and reforms is advisable. Incremental reforms, accompanied by robust monitoring and evaluation mechanisms, allow for the gradual adoption and adaptation of best practices while minimizing potential disruptions and risks. [23]
CONCLUSION:
In summary, this paper sheds light on the pressing issue of liquidity challenges facing Yemeni banks amidst prolonged political instability, economic volatility, and institutional weaknesses. Through a comprehensive analysis of the factors contributing to the liquidity crisis, the timeline of events leading to its escalation, and its profound impacts on banking operations, customer trust, and the broader economy, several key findings and insights have emerged.
Firstly, it is evident that the liquidity crisis in Yemeni banks has been exacerbated by a combination of domestic and external factors, including political unrest, economic disruption, mismanagement of funds, and regulatory challenges. These factors have undermined depositor confidence, constrained lending activities, and posed significant risks to financial stability and economic growth.
Secondly, the paper underscores the critical importance of addressing liquidity challenges for the stability and growth of Yemeni banks. Strengthening liquidity management practices, enhancing regulatory frameworks, and building institutional capacity are essential for safeguarding financial stability in Yemen's banking sector.
Furthermore, the paper highlights several avenues for future research and policy development in this area. Exploring alternative financing mechanisms, promoting financial inclusion, and fostering international cooperation and assistance are potential avenues for addressing liquidity challenges and promoting sustainable development in Yemen's banking sector.
Addressing liquidity challenges is paramount for ensuring the stability and growth of Yemeni banks. By implementing targeted policy reforms, enhancing regulatory oversight, and building institutional capacity, Yemen can overcome its liquidity crisis and pave the way for a more resilient and prosperous banking sector in the future.
[1] "Bank capital and bank stability: The mediating role of liquidity ...." tandfonline.com
[2] "Management of Liquidity and Profitability in Commercial Banks." 10 Mar. 2019, link.springer.com
[3] "Despite Ongoing Challenges, Parties to Yemen Conflict Showing ...." press.un.org
[4] "Yemen's Banking Problems Could Have Dire Humanitarian Implications." 24 Mar. 2017, washingtoninstitute.org
[5] "How financial firms can prepare for the 2024 regulatory landscape." 13 Sept. 2023, ey.com
[6] "Yemen civil war: the conflict explained | Yemen | The Guardian." theguardian.com
[7] South24 Center, (2022, April 3). Central bank and currency deterioration in Yemen. South24 Center. south24.org
[8] "After 9 Years of Conflict, Yemen is Still One of the World’s Worst ...." 26 Mar. 2024, actionagainsthunger.org
[9] "The Global Economic Outlook During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Changed World." 08 Jun. 2020, worldbank.org
[10] "Yemen's Houthis attack al-Dhabba oil terminal, force ship to leave." 21 Nov. 2022, reuters.com
[11] South Center, (2024, March 30). Amid ‘counterfeit’ warning, Houthis issue new 100 riyal coin. South24 Center. south24.org
[12] "Central Bank of Aden: «60 days to move all bank headquarters»." 03 Apr. 2024, south24.org
[13] Central Bank Of Yemen - Aden. (n.d.). Research & Statistics | Central Bank of Yemen - ADEN. Central Bank of Yemen - Aden. english.cby-ye.com
[14] "Liquidity shocks and interbank market failures: the role of deposit ...." 21 Mar. 2021, link.springer.com
[15] "Global Financial Stability Report - IMF." 11 Apr. 2023, imf.org
[16] "تقرير للبنك الدولي يُبرِز التحديات والفرص المتاحة التي ينطوي عليها ...." 30 May. 2023, albankaldawli.org
[17] "Policy uncertainty and bank systemic risk: A perspective of risk ...." 01 Oct. 2023, sciencedirect.com
[18] "Nonbank Financial Sector Vulnerabilities Surface as Financial ... - IMF." 04 Apr. 2023, imf.org
[19] "Yemen Economic Bulletin: Battle to Regulate Banks Threatens to Rupture ...." 27 Nov. 2020, sanaacenter.org
[20] "Explainer: Lebanon's financial crisis and how it happened." reuters.com
[21] "Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) - Executive Summary." 28 Jun. 2018, bis.org
[22] "Central Bank Tools and Liquidity Shortages - Federal Reserve Bank of ...." newyorkfed.org
[23] "Navigating Complex Challenges to Support Yemenis in Times of Compounded ...." 28 Apr. 2022, worldbank.org
Previous article